“Human resources isn’t a thing we do. It is the thing that runs our business.”
— Steve Wynn
Renowned American Real estate Figure
The quote depicts the importance of an HR professional in an organization, who is at the core of every administrative function. The HRM and HRD are the two components derived from the HR department, which accommodate assorted needs. These terms are often used interchangeably.
However, these two departments have contrasting features, roles, and responsibilities, which might not be easily comprehensible.
So here we will decouple them by understanding their meaning and comparing them by analyzing the similarities and difference between HRM and HRD.
What is HRM?
The HRM means managing the workforce to ensure maximal performance while achieving organizational goals. The HRM full form is Human Resource Management, which portrays its essence.
E.F.L. Brech has given its point-blank explanation to depict HRM full form by defining it as “the part of the management process which is primarily concerned with the human constituents of an organization.”
While Dale Yoder has taken the functional viewpoint to elucidate it as the process of planning and directing the development and utilization of human resources.
In a nutshell, it can be portrayed as the management of the workforce and their relationship within the organization.
Its meaning and essence have progressed through multiple stages and evolved over time, which need to be considered in examining its crux.
Evolution of HRM
HRM has not been a monotonous and uniform organizational unit. Several factors have led to its genesis, and it has metamorphosed a lot to come to its current status.
Here is a graphical representation of its evolution.
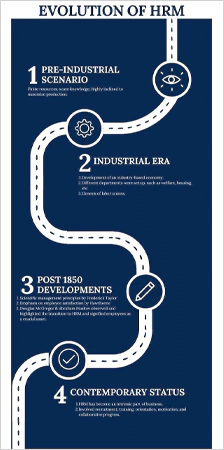
After covering its evolution, the next mooted topic is the function of Human resource managers, described in the subsequent section of this discussion.
Functions of HRM
The functions of HRM can be divided into 2 broad categories, i.e., managerial functions and operative functions. These have been distinguished based on the fundamental roles and duties performed by the HR manager in different organizational domains.
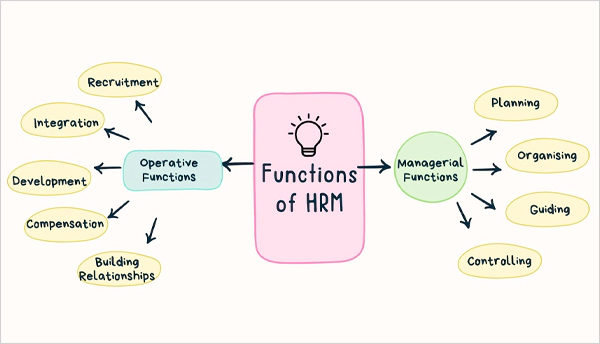
Operative Functions of HRM
In HR management, the operative functions focus on including and assimilating employees into the working culture. Some prominent duties among them are as follows.
- Recruitment: One of the prime operative functions of HRM is to recruit potent employees with the requisite genius and skills for the organization.
- Integration: The HR managers ensure provisions for the enhancement of the workspace environment, better communication among the team, and dispute resolution to check hassles at the nascent stage. This integrates each employee into a working community of the organization as a whole.
- Development: HRM also provides avenues of progress and ensures augmenting productivity and performance through sufficient opportunities.
- Compensation: It becomes the duty of the HRM department to ensure that employees at the same level and yielding the same output must be equally compensated and significantly appreciated.
- Building Relationships: The HR managers also master the matrix of building relations among the workers and between workers and the administration by acting as a mediator and facilitating bargaining.
Managerial Functions of HRM
The HR managers also carry out managerial duties to align the workforce with the broader goals and synchronize the various teams and departments to work in tandem. Some notable managerial responsibilities of HRM are as follows.
- Planning: Devising approaches and strategies for achieving the goals, encompassing all needs such as recruiting, selecting, and other HR requirements to co-create a harmonious work environment.
- Organizing: Restructuring the components of goals, defining responsibilities, and streamlining the goals to achieve common objectives.
- Guiding: Motivating the employees and staff to maximize their efforts by inspiring and leading them, and exploiting their potential effectively.
- Controlling: Comparing the employees’ performance with the objectives of the plan, restructuring the plan, incorporating the changes, and implementing the changes accordingly.
From the above points, we can evidently infer that HRM acts as a buffer between the administration and the workforce.
But for performing such functions, they must possess certain attributes to live up to the standards.
Qualities Necessary for HRM Professional
As the HRM is a polyfunctional unit of an organization, its professionals need to have some skills mandatorily to carry out their functions and actualize the collective objectives.
- Communication Skills: Good and influential communication always leaves a lasting impact. In HR management, such skills help in conveying and grasping thoughts effectively.
- Creativity: Creative solutions to emerging problems and innovative practices to knit the employees together, ripples in toning up the cooperation and collaboration, and keeping up the spirit.
- Dispute Resolution: The varied views and working styles always generate disputes and discontent. To settle them, the HR manager should arbitrate the matter, neutralize the situation, and bring back the prior decorum.
- Leadership Dynamism: One should be efficient in juggling between the tasks without compromising their essence to provide HR services.
All these skills are a quid pro quo in discharging the HRM duties effectively and productively.
The progress trajectory of HRM has been tracing an all-new course. A very productive survey has been conducted by members of the Union Nikola Tesla University to grasp and analyze the trends in HRM and understand the perspective of the sample workforce.
This survey has drawn the following conclusion about the perspective of the HRM professional on the changing nature of this domain.
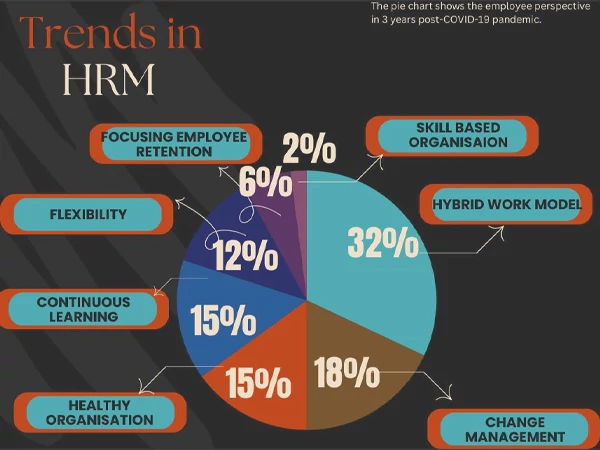
The next perspective to discuss in the sequence is the analysis of HRD.
Let’s analyze it.
What is HRD?
HRD is a strategic approach to improve the capabilities of the employees of a firm and to attain the desired objectives and goals.
HRD full form stands for Human Resource Development, which is the organization’s system and structure that facilitates employees in developing their knowledge, skills, and proficiency.
Getting more precise about it, Giley and Eggland (1989) have defined HRD full form as “an organized learning experience provided by employees to bring about possibilities of performance growth or personal growth within the specified period.”
So, in elementary connotation, HRD professionals buckle down to upskill the workforce for better productivity and performance.
The HRD field has undergone a multistage evolution, which has brought it to its current structure.
Evolution of HRD
Like HRM, HRD has also gone through a series of stages to come up in its contemporary form. These levels have been depicted in a graphical form in the following infographic.
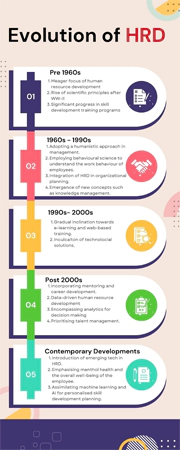
Functions of HRD
To lead the progress in the firm, HRD professionals are obligated to perform certain functions.
- Orientation and Training: The prime function of the HRD department is to conduct orientation and training programs to refine and upgrade the employees’ skills and proficiencies.
- Career Planning: This unit is responsible for talent management, strategizing career development, and conducting performance appraisals. The disclosure and dialogue of aspiration between employees and HRD managers further strengthen confidence and trust.
- Organizational Development: The HRD professionals’ intervention and assistance stimulated individual and collective growth, which is vital in overall organizational development.
- Performance Enhancement: Conducting internal and external talent assessment, gauging employee satisfaction, and elevating the workforce participation cumulatively stimulated the performance enhancement of the team.
All these functions have a macro impact on the efficiency and aggregate output.
The HRD professionals act as a bulwark of progress for an organization, and to perform such versatile roles, they must have some requisite skills.
Necessary Skills and Competencies for HRD
To meet the responsibilities, these professionals must have some essential expertise. Some must-have competencies are as follows:
- Analytical Skills: Analyzing the information and data to ensure talent management, performance evaluation, and deriving the training necessities requires analytical skills in an HRD professional.
- Mentoring Capabilities: The mentoring skills are imperative for the HRD team to dictate the strategy, check deviations, and fine-tune skills to ensure professional development.
- Communication Skills: Being the centerpiece in proficiency enhancement, it demands good communication skills. The process of conducting the recruitment drive, taking interviews, creating job descriptions, negotiating the conditions, etc., needs expressive and unequivocal communication abilities.
- Organizational Skills: Steering talent management and conducting training and orientation require pronounced organizational skills.
These skills are the litmus test for hiring the best HRD professional to drive full potential.
The comparison between HRM and HRD plots the course through the HRM and HRD differences and similarities.
Also Read: How to Become an HR Manager in a Company? (2025)
What is the Difference Between HRD and HRM?
Both the units in an organization have contrasting characters, which bring out the fundamental difference between HRM and HRD. These dissimilarities are worth considering in comparing them.
| Points of Difference | HRM | HRD |
| Basic character | It comes under the management section of the organization. | It is an offshoot of the HRD division. |
| Emphasis | Supervise the general human resources and ensure smooth administrative functioning. | To enhance the skills, knowledge, and competencies of the employees to ensure progress in the organization. |
| Scope | Conducts Employee recruitment, ensuring cordial inter-employee relations, and ensuring compliance with prevailing laws. | Cultivate a culture of training and talent management. |
| Objective | Ensure that the employees are entrusted with the right responsibilities. | Invests in employee training to enhance overall performance and foster growth and progress. |
| Process | Procedures are executed when needed. | Endures as a continuous process. |
| Span of execution | Emphasis on short-term goals. | Highlights long-term strategic planning and prepares employees for long-term progress. |
| Orientation | Emphasize the employees’ needs. | Focus on the organization’s needs to ensure career progress in the organization. |
To have a balanced and holistic comparison, we need to analyze the similarities between them as well.
Similarities Between HRM and HRD
After considering the differences between HRM and HRD, we need to go through the similarities between them as well. These analogies establish coordination between these divisions in an organization and help in mutual teamwork.
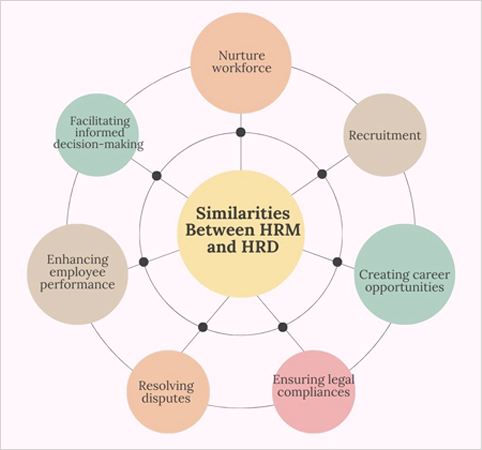
On this note, here are the enunciated similarities between them.
- Plays an instrumental role in nurturing the workforce.
- Recruiting the best talent in the firm.
- Caters to creating career growth opportunities.
- Ensure the enforcement of policy and conform to legal compliances.
- Resolve the disputes and conflicts.
- Strive to enhance employee performance and productivity.
- Employing data and analytics to ensure informed decision-making.
These similarities portray the true picture and help in making precise comparisons and driving definitive insights.
Conclusion
The above discussion has substantiated the comparison and defined the difference between HRM and HRD by countering the speculations and extrapolating using defined information. Undeniably, it will be instrumental in illustrating every aspect concerning these units.
Both departments work as cogs of a wheel by attracting high-caliber professionals, untangling and resolving inter-employee conflicts, and upgrading the proficiency and standard of the employees to secure shared growth.
FAQs
1. How are HRD and HRM related?
Ans: Both HRD and HRM are subdivisions under the HR (Human Resource) department. While HRM maintains personnel management, HRD emphasizes enhancing the proficiency and expertise to ensure the progress of the organization.
2. What does the HRD stand for?
Ans: The full form of HRD is Human Resource Development. It deals with the planning and strategizing of the organizational progress by developing the skills and proficiencies of employees.
3. Who introduced HRD?
Ans: Leonardo Nadler formally introduced the concept of HRD in a conference organized by the American Society for Training and Development in 1969.
4. Who is the father of modern HR?
Ans: Dave Ulrich is considered the father of modern HR. He is a distinguished educator and a renowned mentor who has a profound impact on the HR industry.





