The responsibility of Payroll management rests with the HR teams, who have to oversee all pay schedules of the employees.
Amongst the salary schedules, the monthly payment system is highly favored. Yet, many industries and market sections opt for the semi-monthly wage payment system.
But, do you know what semi-monthly means?
Here, we will discuss the semi-monthly system, its meaning, how it differs from its closest counterpart, the biweekly system, its benefits and shortcomings, its suitability, and how to implement it effectively.
What is Semi-monthly Meaning?

Semi-monthly is a payment system in which the employees are paid twice a month. The employer selects two specific dates in a month on which the salary is credited to the workers.
According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, around 19.8% of the people in the US are paid in a semi-monthly system.
The calendar displayed below is a template of a month depicting the pay period and pay day of an employee paid semi-monthly.
| Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday | Saturday | Sunday |
| 1 (Payday) | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 (Payday) | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
Here are some more precise details that will explain to you the semi-monthly meaning more comprehensively.
- Pay Periods: A month is divided into 2 pay periods. For example, the 1st to 15th and the 16th to 30th dates of a month. This makes 24 pay periods in a year.
- Payment Frequency: The employee is paid twice a month on specific pre-decided dates. For example, the 1st and 15th of every month.
- Annual Paychecks: Every worker will receive 24 paychecks annually. (12 months x 2 paychecks a month = 24 paychecks)
These simple points will help you understand what semi-monthly payroll is.
This payroll type resembles a bi-weekly system, but both differ on many grounds.
Suggested Reads: Bimonthly vs Biweekly Payroll – What You Need to Know in 2025
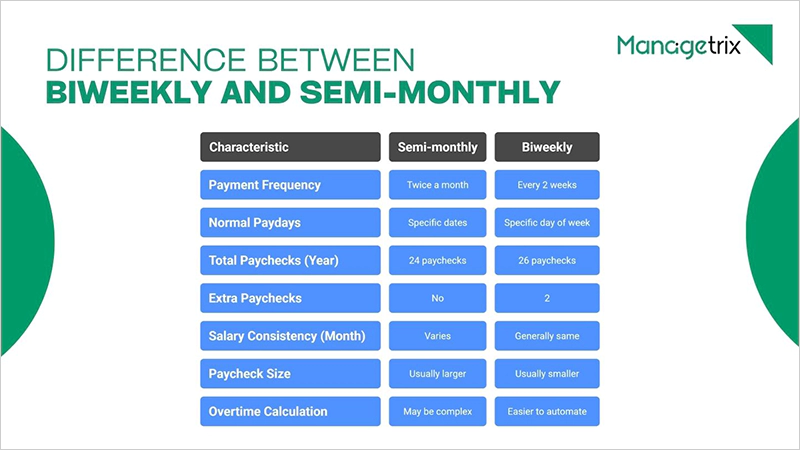
Difference Between Biweekly and Semi-monthly
Biweekly is another wage payment system prevalent in the market. But it has some minor conceptual differences from the semi-monthly system.
If you closely understand the word “Bi-weekly”, you will learn that the employee will be paid for 2 weeks, i.e., 14 days, irrespective of the monthly or annual payment frequencies.
For example, your firm may decide that the workers will be paid once in 2 weeks, then the payroll will be called bi-weekly.
Let’s understand it through an example.
Assume a company, XYZ, decides to pay its employees on every other Saturday, i.e., once in 2 weeks. Then their payroll calendar will look as follows.
| Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday | Saturday | Sunday |
| 1 | 2 (Payday) | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 (Payday) | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 (Payday) |
Payroll colander of company XYZ
The survey conducted by the US Bureau of Labor Statistics mentions that this system is the most opted for by firms in the US, with 43% of people being paid this way.
Now we will differentiate these two types to understand the semi-monthly meaning holistically.
| S. No. | Differences | Semi-monthly | Biweekly |
| 1 | Payment Frequency | Twice a month | Every 2 weeks |
| 2 | Normal paydays | On specific dates like the 1st and 15th of a month. | On a specific day of the week, like every other Saturday |
| 3 | Total paycheck, a year | 24 paychecks | 26 paychecks |
| 4 | Extra paychecks | No | 2 |
| 5 | Salary consistency in a month | Varies based on the paydays | Generally remains the same |
| 6 | Paycheck size | Usually larger than biweekly | Usually smaller than semi-monthly |
| 7 | Overtime calculation | May be complex | Easier to automate |
Benefits of the Semi-monthly System
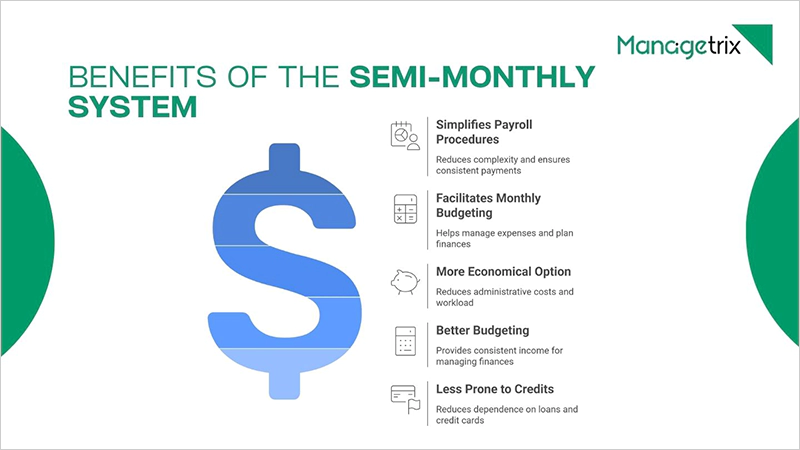
The semi-monthly salary system has been fairly opted for by the firms owing to its advantages over other wage payment systems. These benefits have led the US states of Arizona, Kentucky, and Georgia to shift to this wage payment approach.
As an HR, you must understand how it is beneficial to employees and employees in different ways.
For Employers
- Simplifies Payroll Procedures: It reduces payroll complexity by aligning with calendar months, simplifying processing, and ensuring consistent and predictable payments.
- Facilitates Monthly Budgeting: Employers can manage expenses with income cycles, facilitating financial planning, cash flow management, and deriving accurate forecasting for business operations.
- More Economical Option: Processing payroll 24 times a year reduces administrative costs and workload compared to bi-weekly or weekly payrolls.
For Employees
- Better Budgeting: Semi-monthly pay provides a consistent twice-monthly income, helping employees easily manage bills, expenses, and savings with regular monthly payment cycles.
- Less Prone to Credits: With predictable incomes twice a month, employees manage expenses better, reducing dependence on loans, credit cards, or overdrafts for bills.
Now, let’s discuss the shortcomings of this arrangement to learn the semi-monthly meaning better.
Shortcomings of the Semi-monthly Pay Schedule

The semi-monthly system also has certain loopholes that demand your attention in the discussion. These drawbacks are different from the perspectives of the firm and the worker.
Here are some notable shortcomings of the semimonthly pay schedule for the employers and the employees.
For Employer
- Cash flow Issues: Semi-monthly payroll can cause cash flow challenges, requiring careful planning to ensure funds are available when paychecks are due.
- Complex Procedure for Hourly Employees: Managing payroll for hourly workers becomes complicated, especially calculating overtime across irregular semi-monthly periods.
- Not Workable for Volatile Industries: The industries like hospitality and retail, which experience high staff replacement, won’t fit in this salary system.
For Employees
- No Extra Paycheck: Unlike biweekly pay, semi-monthly schedules don’t provide extra paychecks.
- May Result in Uneven Pay Periods: If the pay days are not specified, then the public holidays and weekends falling on the pay days can disrupt the payment schedule.
Is Semi-monthly Ideal For Your Business?

Being an HR, you should learn about whether the business is fit to opt for a semi-monthly pay schedule or not.
After discussing “what does semi-monthly mean”, we will discuss whether it is ideal for your business or not.
Firstly, carefully review operations, workforce type, and company capability, and decide if semi-monthly pay fits the business needs. This pay schedule works well for some businesses, but may not suit others, depending on their nature.
If most employees are recruited on a fixed salary basis, then semi-monthly payroll aligns well with fixed monthly cycles and is simpler to manage the monthly net pay.
Hence, businesses with stable payroll systems and salaried staff benefit most from semi-monthly payment plans. Its reduced payroll processing frequency allows HR teams to have more time for strategic activities while maintaining steady pay timelines.
Let’s take an example of the US Military Payroll. The US Army is paid twice a month, once in the middle of the month and the other at the end. The dates may vary based on the days of the month and have been made available on the official page of the US Defense Finance and Accounting Services.
So here are some supplementary points that you need to ponder over while deciding if this system favors the firm’s demands or not.
- Efficiency of Payroll Management Team: Consider your payroll team’s ability to handle different pay period lengths and overtime calculations within semi-monthly parameters.
- Adhere to Firms’ Norms: Analyze industry norms to stay competitive in attracting and keeping new talent.
- Appraise Employees’ Preference: Assess employee preferences to ensure the payment schedule supports their budgeting and cash flow needs effectively.
However, this wage payment system will not be ideal for some firms for certain reasons.
- Not Suitable for Hourly Workers: Semi-monthly pay may be less ideal for organizations with many hourly workers due to complicated overtime calculations.
- Inefficient for Certain Industries: Industries like retail, construction, or restaurants often require weekly payroll, so semi-monthly pay may not match employee expectations.
To counter these shortcomings and the pain points, next, we will discuss how to make this system work effectively in your company.
How to Make the Semi-monthly Payment System More Effective?

Semi-monthly pay periods can be structured more effectively to match the requirements of an employer and an employee.
Here are some points to follow to elevate the productivity of this payment schedule.
- Use Best HR Management Tool: Employing the best tool, such as Managetrix HR management tool, will simplify the payroll management for all types of pay schedules, especially the semi-monthly system.
- Consider Fixed Pay Days: Maintain fixed pay dates consistently so both employees and the HR department can plan and manage finances easily.
- Adhere to Local Laws: Understand and comply with your state’s labor laws related to wage payment timelines.
- Communicate the Changes in Pay Days: Inform employees ahead of time if payday shifts due to holidays or weekends to avoid potential confusion or issues.
- Have Flexible Payment Options: Make sure the firm has provisions for flexible payment options for emergencies or unexpected cash needs outside the regular semi-monthly schedule.
Conclusion
The above discussion elaborates on the semi-monthly meaning and why it is beneficial to adopt it. However, before adopting this system, make sure it suits the employment type and management of the firm. As an HR, you must inculcate and implement the best practices mentioned above to make it more effective and productive in your firm.
Next Read: How Many Work Hours in a Month? Average & Calculation Guide
FAQ
1. Is semi-monthly every 2 weeks?
Ans: No, Semi-monthly does not pay every 2 weeks. In this arrangement, the employees are paid twice a month, usually on fixed dates, unlike bi-weekly pay, which occurs every 14 days.
2. How is semi-monthly pay calculated?
Ans: Semi-monthly pay is calculated by dividing an employee’s annual salary by 24, resulting in two equal payments every month.
3. Is a semi-monthly salary paid in a month or in a year?
Ans: Yes, semi-monthly salary is paid twice each month, totaling 24 pay periods in a year, while a monthly salary offers only 12 payments, distributed once per month.
4. Do semi-monthly payments save money?
Ans: Semi-monthly payments don’t reduce expenses directly but may help employees manage budgets better, as they receive consistent twice-monthly income rather than waiting for longer monthly.





